Any business owner is in an ongoing pursuit of the best service and enhanced customer experience. There is no denying that constant improvements in business operations play a crucial role in this battle. Depending on the scale of the business and its inner processes, the company stakeholders may address various means to achieve operational excellence.
In this article, we will consider 2 terms that very often go hand-in-hand together, when it comes to business or process improvements – Business Process Management and Robotic Process Automation.
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
BPM and RPA: 4 key distinctive features and 4 use cases
RPA and BPM: making the right choice
Due to similar aims, these two systems are very often confused. Our mission would be to enhance clarity on the 2 terms and help you understand the difference between them with examples and use cases.
What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
Mordor Intelligence says that BPM market was evaluated at $3.38 billion in 2019 and is expected to reach around $5 billion by 2025″
But what is so good about BPM?
In a nutshell, Business Process Management aims at increasing business productivity by re-engineering the underlying business processes. The essence of the BPM is various business scenarios’ analyses, constant improvements, and optimization.
Gartner defines BPM as a discipline that uses various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, and optimize structured or unstructured business processes.
BPM strategy is achieved through:
- defining the scope of administrative tasks required for the process management
- defining and detailing all the work processes
- identifying weak areas for improvements and optimization
- transforming the current workflows into the more efficient ones
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?

Following the idea of technological impact within BPM, we cannot ignore Robotic Process Automation, a technology that helps automate mundane, repetitive tasks. RPA can be an integral part of the BPM strategy.
It can be illustrated on a workflow level:
While BPM is an approach of revealing weak areas in the workflows, RPA is a technical solution that can eliminate those weak areas taking up the burden of time-consuming, repetitive tasks and freeing up employees’ time for more complex, analytical, and value-added activities within the processes.
The ultimate mission of RPA is to replace manual processes executed by humans with bots.
Hence, Robotic Process Automation is more about automating business processes on a surface level with no deeper involvement, and BPM is about defining low efficient processes at a deeper level and optimizing them.
BPM and RPA: 4 key distinctive features and 4 use cases
The difference between the 2 terms can be simplified and illustrated in the infographic below:
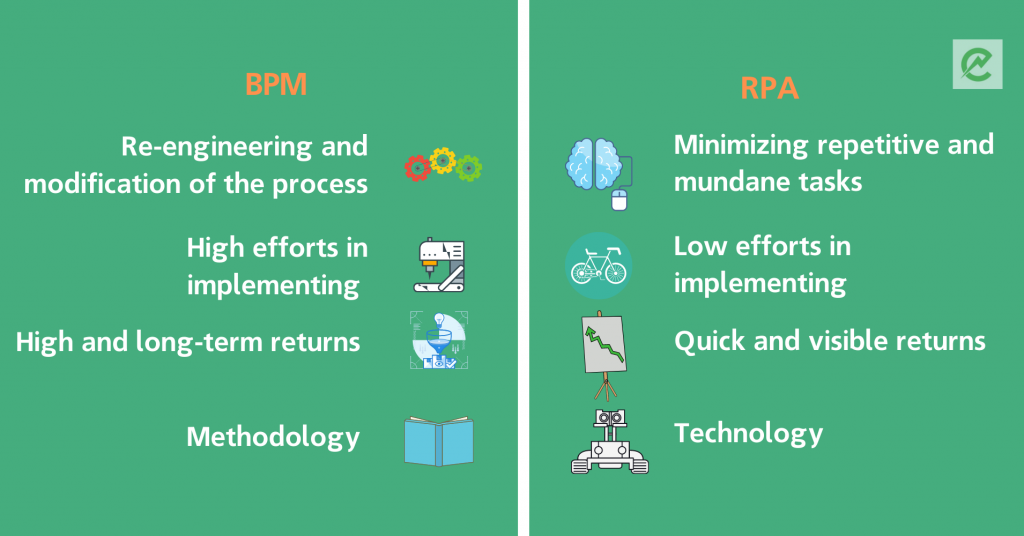
As both RPA and BPM are focused on improved processes and increased productivity, very often, they can be a perfect match and excellently complement each other.
The complementary nature of the 2 terms can be exemplified by 4 use cases below.
1. RPA is for rules, and BPM is for exceptions
RPA is a perfect tool for logical tasks, and there is no secret that it works properly when it comes to the structurally organized, rule-based activities. However, there are no rules without exceptions. Robotic exception, to be more precise.
A good example may be found in the HR onboarding process:
In RPA, a bot may face missing information or a field while fulfilling new employee details. A bot will skip it having determined it is a robotic exception and will keep processing the rest of rule-based task activities.
In BPM, some of such exceptions may be pre-defined and modeled. For instance, when some field is missing, an exception business process would be created. i.e, it would notify the user/administrator about the exception. Having a queue of exceptions can help the team to get information about them immediately, and they can be dealt faster
2. RPA for reducing time on labor-intensive tasks within BPM
BPM is a well-known process of defining a flow or a function to increase operational efficiency. However, sometimes there are tasks within a cycle that can slow down the overall process’s pace.
HR onboarding process can stand as a good example here as well. What does the hiring process typically look like?
- The HR team searches for an appropriate candidate
- The HR specialist interviews him/her and concludes a contract
- The employee provides with the details
- Then it should be entered into the accounting system for payroll processing.
The last stage would be the most labor-intensive since all the data would be copy and pasted into the external accounting system. Here is when RPA can take the burden of manual tasks and significantly improve the process by reducing time. A bot would be created to automate the copy-pasting task, which would reduce the operational cycle significantly.
3. BPM for decision-making processes
BPM can help organize the process of efficient handling of tasks when it comes to more sensitive issues such as privileged access data, for instance.
An example can be found in the field of accounting, where an RPA bot finds a transaction that goes beyond the pre-defined amount. A bot identifies this case and determines it as a task requiring human decision-making.
This case is assigned to a human to be manually observed and processed, and BPM comes in handy.
In scale, exception management can be processed with a separate low-code application that gathers it from RPA and assigns it to human process managers. After assigning, it monitors the date and time of execution.
4.BPM and RPA for 24/7 workflows
Some workflows with no exaggeration can be executed 24/7 if we combine RPA and BPM.
For instance, order processing is not always a straightforward process executed in only 3 steps:
- CRM data entry
- ERP order creation
- Processing order
In the context of a broader business processing, when we need to add some additional steps (e.g. data enrichment when we enrich customers’ data with the use of the external applications) within BPM, we can re-engineer the tasks and automate the whole process by using RPA when it is necessary.
Here how the same process will look like in a more complex yet realistic operational model:
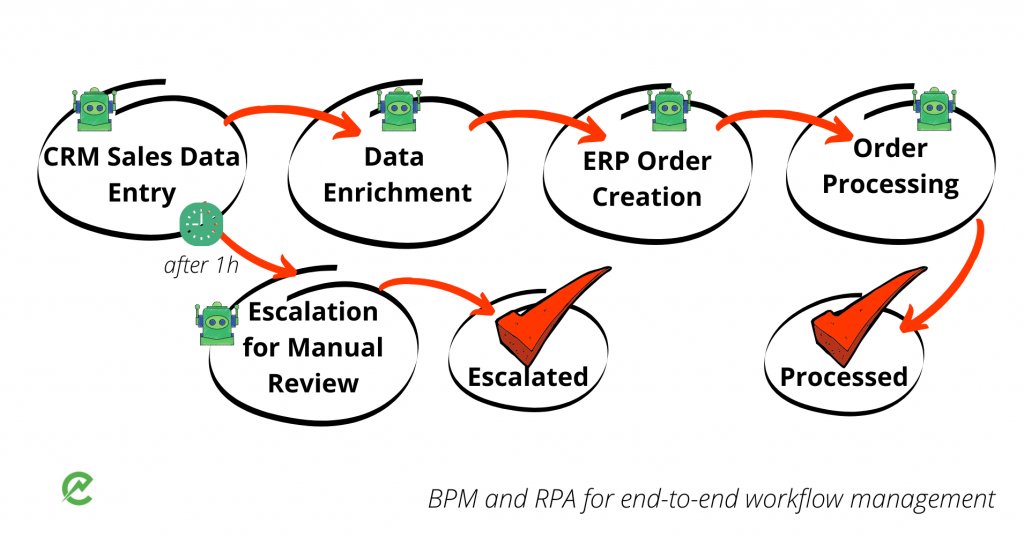
We have not removed an RPA tool here but integrated it with BPM as a part of the end-to-end business process, having made the cycle ongoing.
RPA and BPM: making the right choice
In this article, we tried to enhance clarity on what exactly RPA and BPM are and how perfectly they can be combined.
If you are still stuck with the right technology for your workflows, it would be right to address your business needs and business scale.
However, very often, there is no need to choose between these 2 solutions; instead, it is reasonable to combine them. The complementary approach to BPM and RPA allows you to achieve a more sophisticated and deliberate process management strategy. It begins with setting up goals and identifying automation areas and ending with the estimation of the results and sound decision-making within your company processes.
Combination of robust Business Process Management implying such automation tools as RPA would be more than enough to reach operational excellence.
Here in Electroneek, we are perpetually striving to help our customers follow their BPM tactics. If you are ready to bring these positive changes to your organization, book a demo, and discover how to enhance your business operations today!