What is RPA
Find out how robotic process automation technology works
RPA for MSPs
Learn how RPA enables MSPs to increase their value
History of RPA
Discover the history behind RPA, as we know it now
What is OCR
Unpack how OCR lets MSPs and their clients make digital transformation easier and more productive
What is iPaaS
Get a grip on what iPaaS technology does and how it can aid your MSPs and end clients with integration tasks
What is AI
Find out how AI technology functions and the numerous ways it can help your MSP and clients succeed
Platform Overview
ElectroNeek’s ecosystem from the bird’s eye view
Studio Pro
Integrated Development Environment to build RPA bots in no time
SaaS Orchestrator
A cloud tool to manage your automated workflows
MSP Toolbox
Explore the various great tools we provide to ensure your MSP and clients succeed
Bot Runner
Free to download app to run RPA bots
Community Forum
Get guidance from ElectroNeek users or share your own insights with your peers
Product Training
Learn how to build great automations with tutorials for beginners and experts
Case Studies
Learn the results ElectroNeek users achieve
API Documentation
Leverage the ElectroNeek API to build all possible integrations with any third-party system
Help Center
Find answers to the most common product-related questions
Security
Find out how we ensure your MSP’s data and information remains secure at all times.
The Evolution of RPA: A 30-Year Journey
From UI testing and the enterprise sector, Robotic Process Automation has made a long way and is definitely here to stay. Discover the history that stands behind RPA, one of the most debated trends today.
RPA: From UI testing to
enterprise and RPA-as-a-service
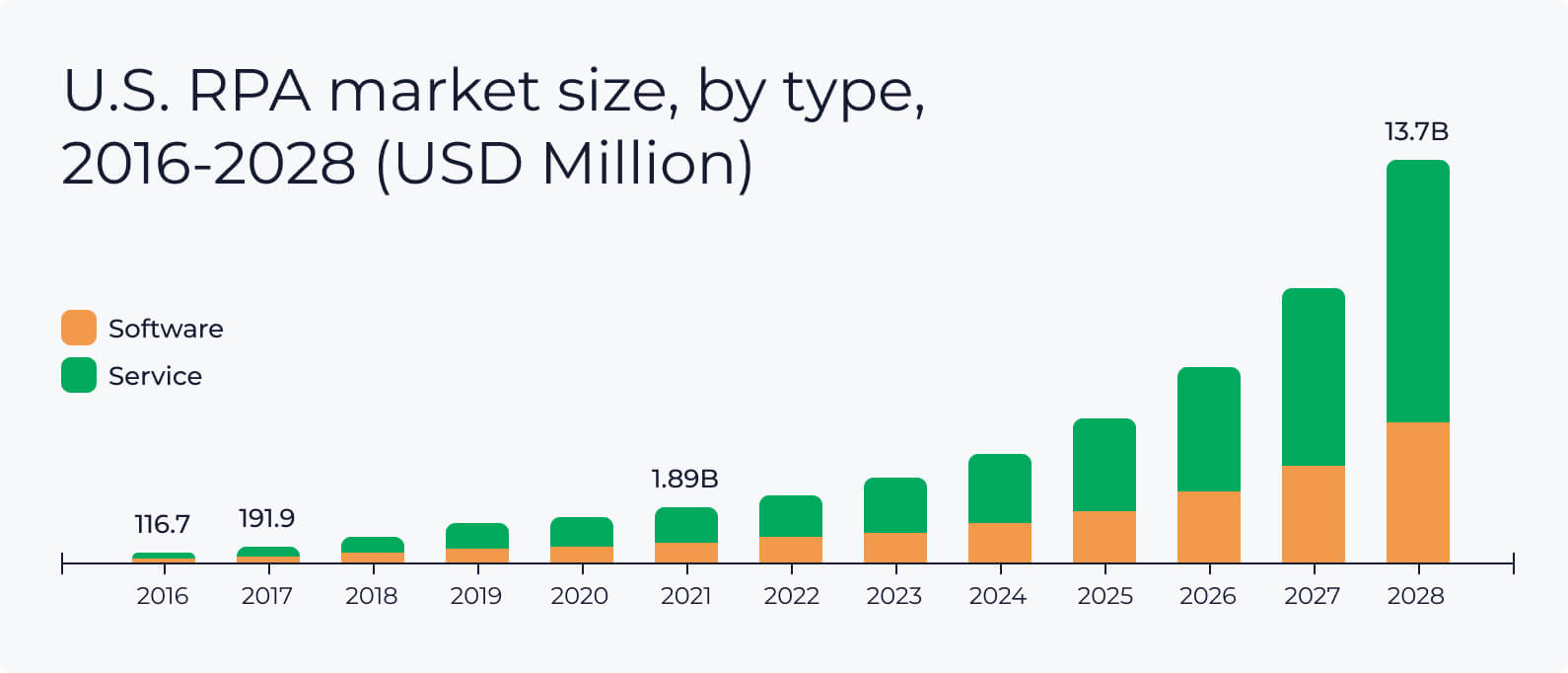
Source: www.grandviewresearch.com
Modern end-to-end automation has come a long way to become the new black. This section unfolds the history of RPA and traces the technology adoption over time. By taking this journey, you’ll also learn why RPA is a strong driver of accelerating the future of fully digitally transformed businesses.
The history of RPA
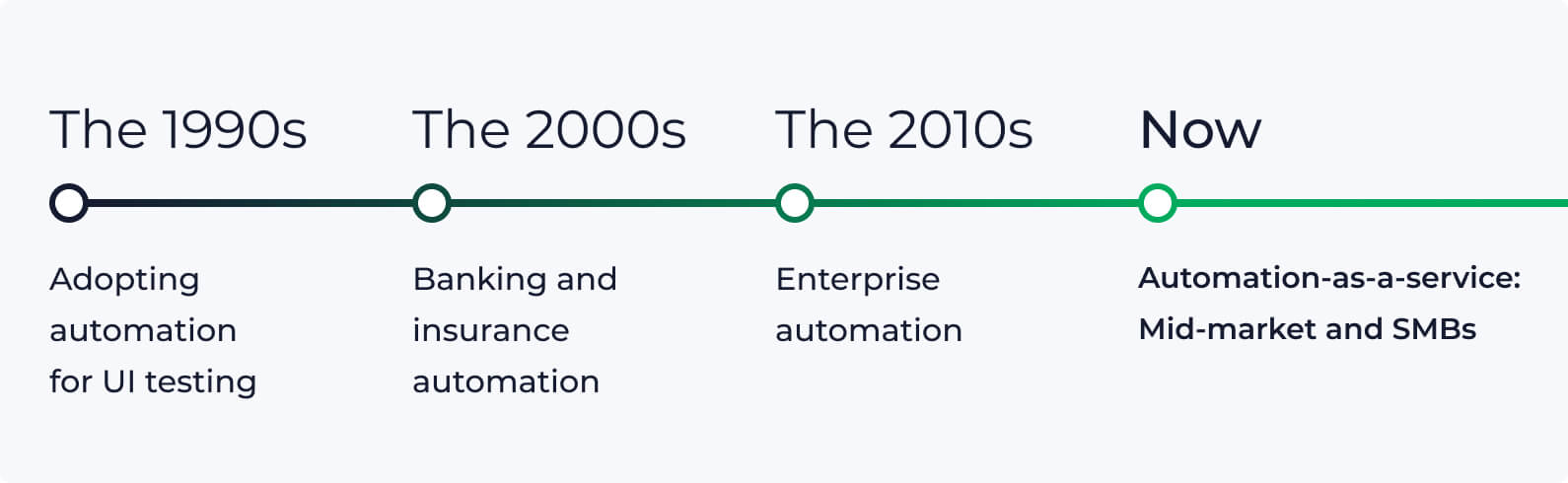
The 1990s: Adopting automation for UI testing
The story of RPA started with the automation of user interface (UI) testing. It usually means testing visual elements of interfaces to make sure they work correctly and a user won’t encounter any issues working with the app.
Back in the 90s, there were few computer models on the market, especially compared to nowadays. However, the primary typical computer user persona started to shift from huge corporations’ and governmental organizations’ employees to ordinary home-based users. This was largely due to the emergence of Windows 95, the canonical operating system of that time. As a result, the shift kickstarted UI testing development as the requirements and screen sizes became more diverse.
At the end of the 90s – early 2000s, companies came to the agile development concept, one of the key values of which is the prioritization of people over processes and tools. Organizations also recognized the need to speed up their operations to stay competitive in the marketplace. Thus, out of necessity, various UI testing and quality assurance (QA) automation scripts were born.
The 2000s: Banking and insurance automation
No wonder that banks and insurance companies were among the first ones to embrace the idea. Industries like these were becoming more subject to regulation, and RPA was a good way to reduce the amount of paperwork and improve compliance.
Another reason why banks and insurance companies were the pioneers of automation is that they had resources available. However, automation technologies still had their drawbacks. One of them was a high entry threshold. If a company wanted to automate its processes at that time, it would likely result in building a complex IT environment. The latter required expensive engineering skills and time-consuming integrations.
The 2010s: Enterprise automation
The real pivotal point for the RPA technology occurred around 2012 when the technology was finally officially recognized by large-scale businesses. There was a combination of factors that made it possible, such as:
- Businesses were looking for ways to reduce their expenses in light of the recent financial crisis.
- Businesses realized the need for digital transformation, and RPA was considered an easy and affordable (in corporate rates, of course) solution for going digital.
These factors led to RPA taking the world by storm, as more and more enterprises started adopting RPA for their mission-critical tasks.
Now: Mid-market and SMB automation
The 2020s are truly the time of RPA democratization and the growing impact of RPA on all segments of economics. The democratization is possible through the gradual departure from costly licensing fees previously only affordable to enterprises, to building partnerships with managed service providers to enable the RPA-as-a-service model. It allows the RPA technology to expand to smaller businesses and provide SMBs with massive productivity outcomes.
In fact, we already see more and more evidence of RPA in SMBs moving from pilots and proof of concepts to real-time production in much shorter times than Enterprises do. According to the 2021 report by Xerox, one of the largest ElectroNeek’s partners, 80% of SMB leaders saw automating tasks and processes as important to their survival with two-thirds planning on upgrading their automation tools.
Demographics is also key. Since millennials (and already zoomers) started their careers, they wanted interesting, challenging tasks, not monotonous jobs. With the help of RPA bots, companies can easily automate the work of many departments and specialists. It means, when automation is efficiently implemented for tedious, repetitive tasks, employees become more efficient compared to previous years.
Such changes in demographics along with an MSPs’ focus on building recurring revenue drive the popularity of a bots-by-subscription business model. With this model, clients make periodic payments to MSPs instead of solid upfront costs, which allows an even wider variety of companies to access the benefits of RPA.
Future of automation: Automation-as-a-service
As automation-as-a-service continues to be the major driver for RPA market growth, RPA will penetrate more companies of all sizes with the help of managed service providers. RPA workflows will leverage more technologies from a hyperautomation stack, such as optical character recognition and computer vision. These technologies, brought by MSPs to their clients through integrations with RPA platforms, will enable a much broader automation-as-a-service market that will outgrow and outperform RPA as we know it today, potentially including physical robotics with a robot-as-a-service model.
The future of work is automation, and the future of automation is service-based. Managed service providers will continue to drive the change in the market, bringing together complex technologies and skilled talent to better serve their client needs.
The bottom line
If you are a managed service provider, discover how MSPs provide RPA services and explore opportunities to start an RPA business by partnering with ElectroNeek. If you consider RPA for your company, find a trusted RPA Service provider within the ElectroNeek Network and start your RPA journey on the business terms that makes sense to your business.
Table of contents